Your Online HERS Rater Training Center
FREE HERS RATER PRACTICE EXAMPUT YOUR HOME PERFORMANCE BUSINESS ON ROCKET FUELENERGY AUDITOR NEWSLETTERGet the only Energy Auditor Marketing Newsletter with monthly strategies and tactics to grow your home performance business.
|
Building Science Fundamentals4. Heat Gain / Loss: Internal, Solar, Heat Transmission, Air Leakage
There are several ways the outside heat or cold gets into our homes. Keep in mind that these heat gains or heat losses all follow the Second Law of Thermodynamics where:
Knowing the methods of heat gain or loss, the Second Law of Thermodynamics and with some good detective work during your energy audit (pressure mapping and a thorough attic inspection) you will be on you way to becoming an expert energy auditor. Methods of Heat Gain and Heat Loss1. Internal- heat gains are from wasted energy (unconverted energy) from heat given off from light bulbs, appliances, stored heat energy in furniture and carpet and our bodies.
2. Solar- heat gains are from the suns radiant energy and primarily enter our homes through the windows (heat always goes in the path of least resistance). Solar heat gain can also be through our walls.
3. Heat transmission- occurs by conduction, convection and radiation. Conduction is heat transfer from direct contact of two objects, like a frying pan heating your food from the stove. Thermal bridging is a popular energy auditor term for conduction where heat flows in the path of the least resistance. So in a wall, for example, heat will go to the weakest R-value of a wall composition, which is the studs. This will show up on a thermal camera as a red color, indicating more heat transfer through the studs than a wall cavity filled with insulation. Convection heat transmission occurs through the air or water droplets. The stack effect is an example of convection where warm air rises and cold air falls. Convection is driving by two things... a hole (leakage path) and a pressure difference (wind, AHU, fans, stack effect). Without one, you don't have the other and convection is taken out of the equation. Radiation heat transmission occurs through space and can be from either solar radiation or infrared radiation. Examples of radiation are a hot wall radiating heat after the sun sets or a person feeling cold next to a window in the winter because they are radiating their heat to a colder surface.
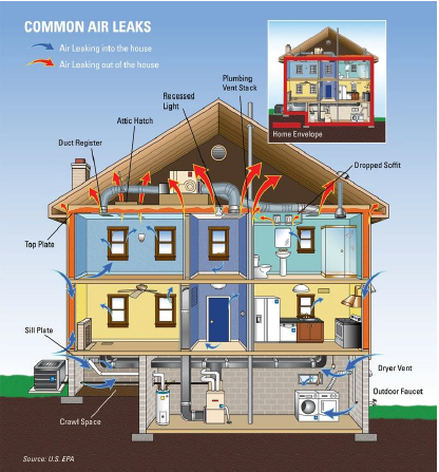
4. Air leakage- is caused by holes in our home that are connected to the outside. Common sources of air leaks are around recessed canned lights, exhaust fans, ceiling fans, windows, doors, duct registers, electrical outlets, light switches, plumbing penetrations behind the toilets, plumbing lines under the sink, door frames, sliding doors, and doggie doors.
Next Section1a. Basic terms and definitions
1b. Principals of energy, air & moisture
1c. Combustion science
|